Cloud adoption has become synonymous with modern IT strategy, but security remains its Achilles’ heel. In 2024, breaches affected major enterprises, resulting in millions of compromised records and significant financial damage. IBM’s Cost of a Data Breach 2024 report highlighted that the average cost of a breach reached $4.88 million which underscored the immense stakes at play.
To complicate matters, attackers have evolved their methods. Sophisticated supply chain attacks now target cloud-based workloads, while ransomware has grown more persistent, often leveraging weak IAM policies or overlooked configurations.
For organizations using AWS, understanding the AWS Shared Responsibility Model is foundational. This model clearly delineates what AWS secures and what customers must protect. Missteps—such as assuming AWS automatically encrypts all stored data—can open the door to catastrophic vulnerabilities.
Understanding the AWS Shared Responsibility Model
The AWS Shared Responsibility Model is more than just a guide—it’s your roadmap to a secure cloud environment. At its core, it’s about teamwork: AWS takes care of securing the cloud infrastructure, while you, as the customer, handle protecting your data, applications, and configurations. This clear division of tasks helps ensure that nothing falls through the cracks.
Understanding the AWS Shared Responsibility Model is essential for anyone using AWS. While AWS provides a strong foundation—like securing data centers and offering powerful tools to manage access and encryption—it’s up to you to use those tools effectively. Whether it’s setting up proper permissions, encrypting sensitive data, or monitoring for unusual activity, your role is just as critical as AWS’s.
By working within this framework, you not only strengthen your defenses but also create a solid plan for managing cloud security responsibilities. This proactive approach helps you meet compliance requirements, reduce risks, and build a more secure and reliable cloud environment.
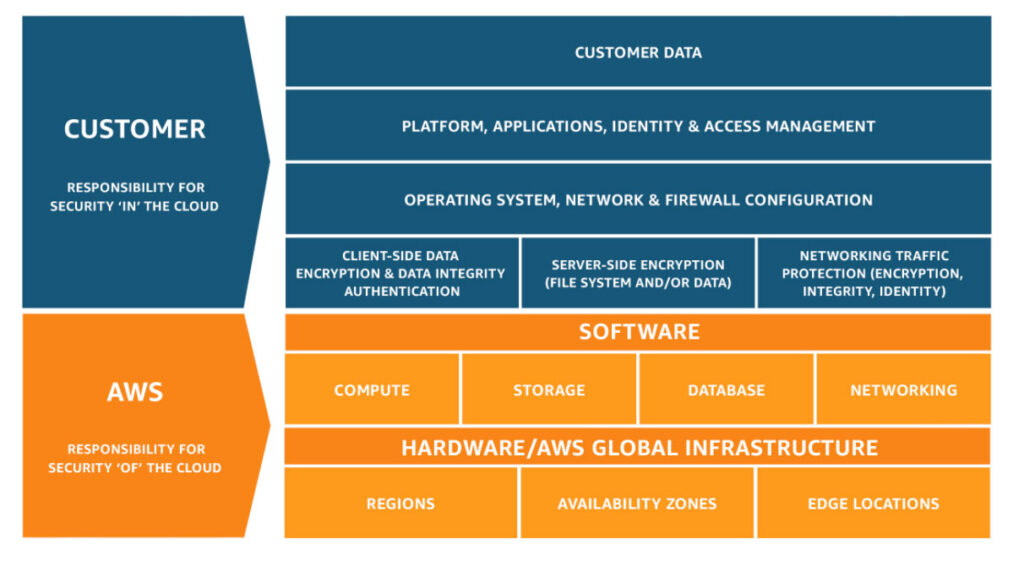
Figure 1: The AWS Shared Responsibility Model (Source: aws.amazon.com)
Security OF the Cloud (AWS Security Responsibilities)
Under the AWS Shared Responsibility Model, AWS is accountable for securing the infrastructure that supports its cloud services. This includes the physical hardware, networking, and software systems that run AWS services. By addressing these cloud security responsibilities, AWS ensures a strong foundation for customers to build their workloads confidently.
1. Physical Data Center Security
AWS data centers are fortified against both physical and environmental threats. Facilities incorporate advanced power redundancy systems. AWS operates highly secure global facilities with biometric access controls, 24/7 surveillance, ISO 27001-certified environmental protection, and advanced redundancy systems, including UPS and waterless fire suppression.
2. Network Security Innovations
AWS Shield Advanced has been updated to counter large-scale DDoS attacks, integrating machine learning (ML) models trained on global attack data to detect anomalies in real-time. AWS uses custom-built silicon through the Nitro System and advanced routing protocols to secure its hardware against tampering and ensure reliable network operations.
3. Hypervisor and Isolation Technologies
The AWS Nitro System, now central to Amazon EC2 instances, offers hardware-enforced isolation, ensuring customer workloads are isolated at the chip level. In 2025, AWS introduced Nitro Enclaves, which allow customers to process sensitive data securely without exposing it to the broader environment.
4. Network Security Innovations
AWS uses custom-built silicon through the Nitro System and advanced routing protocols to secure its hardware against tampering and ensure reliable network operations.
With these AWS security controls in place, the infrastructure is resilient, secure, and aligned with global compliance standards. By addressing its cloud security responsibilities, AWS provides customers with a strong, reliable foundation to confidently secure their own workloads and focus on meeting their organizational objectives. This shared partnership is the cornerstone of effective security on AWS.
Security IN the Cloud (Customer Security Responsibilities)
In the AWS Shared Responsibility Model, customers play a crucial role in securing their workloads, configurations, and data within the cloud. While AWS ensures the foundation is secure, the customer’s cloud security responsibilities lie in protecting what they deploy and build. This shared approach creates a comprehensive cloud security model, but success depends on understanding and actively managing your part.
1. Data Encryption, Backup, and Security
Securing data is a non-negotiable. Customers can:
- Simplify key management and centralize control of encryption keys with AWS Key Management Service (KMS).
- Leverage dedicated hardware appliances for cryptographic operations with AWS CloudHSM.
- Back up critical data and test recovery plans regularly to ensure continuity.
- Enable Amazon S3 Versioning and Cross-Region Replication for high availability and disaster recovery.
- Use Amazon Macie to monitor sensitive data and identify potential exposure risks.
Advanced Practice: Use Envelope Encryption to protect keys further, layering customer-controlled keys over AWS-managed encryption.
2. Identity and Access Management (IAM)
- Use AWS Identity Center (formerly AWS SSO) for centralized access control across AWS accounts.
- Integrate session-based policies to enforce time-limited access for sensitive operations.
- Implement multi-factor authentication (MFA) and strong password policies.
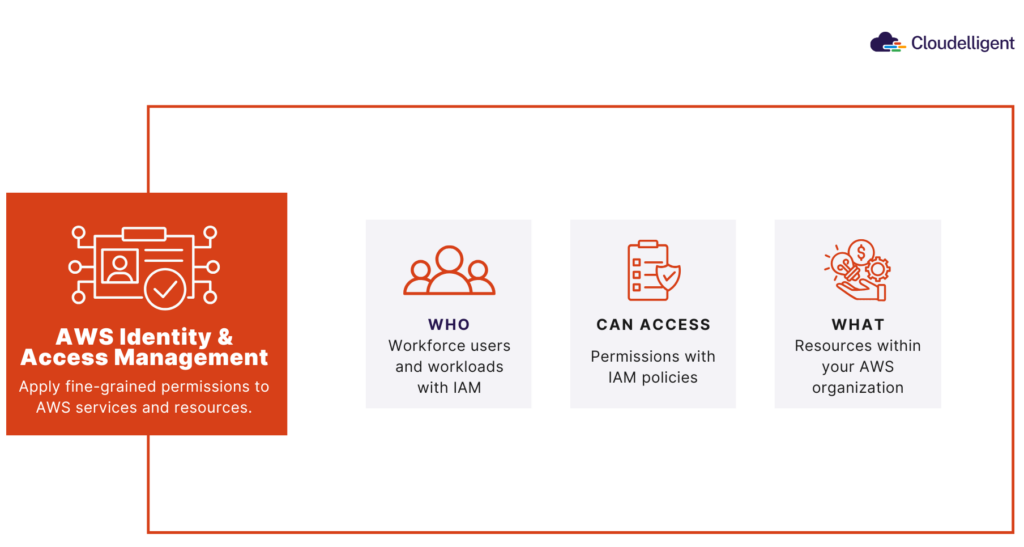
Figure 2: IAM Policies Overview
3. Operating System Security and Firewall Configurations
- Automate OS patching using AWS Systems Manager Patch Manager.
- Deploy host-based intrusion detection systems such as CrowdStrike, alongside AWS Inspector.
- Use AWS Shield and AWS WAF for additional protection against DDoS and web application attacks.
4. Application Security
- Secure APIs with Amazon API Gateway, leveraging throttling and AWS WAF (Web Application Firewall) to mitigate abuse.
- Regularly run static and dynamic code analysis tools like SonarQube or AWS CodeGuru Reviewer for vulnerability detection.
5. Network Security
Ensuring robust cloud infrastructure security for networks is a key responsibility.
Figure 3: Network Security on AWS (Source: aws.amazon.com)
- Configure Virtual Private Cloud (VPC) settings, including security groups and Network Access Control Lists (NACLs), to restrict unauthorized access.
- Configure firewalls and security groups to allow only necessary traffic.
- Use AWS Network Firewall to create advanced rules for traffic filtering, intrusion prevention, and anomaly detection.
- Secure connections with AWS PrivateLink to keep communications within your VPC and eliminate exposure to the public internet.
6. Monitoring and Logging
Visibility is critical for identifying and mitigating threats:
- Use AWS CloudTrail to log all API activities, providing an auditable trail for all user actions in your environment.
- Monitor real-time metrics with Amazon CloudWatch and set up alarms for unusual spikes or anomalies in resource usage.
- Leverage AWS GuardDuty for continuous threat detection and AWS Security Hub for centralized management of security findings.
These tools not only enhance security on AWS but also help maintain compliance and operational visibility.
7. Compliance
Maintaining compliance with industry standards is a vital aspect of cloud security governance:
- Use AWS Config to ensure your resources adhere to compliance policies like PCI DSS, HIPAA, or GDPR.
- Automate compliance checks with AWS Audit Manager, which provides frameworks and evidence collection to simplify audits.
- Access compliance certifications and reports through AWS Artifact to ensure alignment with AWS security compliance requirements.
By actively managing these areas, customers fulfill their cloud security responsibilities and align with AWS security best practices.
Service-Specific Responsibilities
AWS offers services across IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS, each requiring a nuanced approach to security. These service types assign distinct cloud security responsibilities to customers, who must actively safeguard their workloads while AWS handles the underlying infrastructure.
1. Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS)
AWS delivers foundational building blocks (e.g., Amazon EC2, Amazon EBS), but customers must:
- Manage network Access Control Lists (ACLs) and security groups.
- Use Network Access Analyzer to validate Virtual Private Cloud (VPC) configurations.
2. Platform as a Service (PaaS)
While AWS handles operational management, customers should secure configurations:
- Enable Amazon RDS encryption at rest and enforce Transport Layer Security (TLS) in transit.
- Regularly audit database access and backup policies.
3. Software as a Service (SaaS)
SaaS simplifies infrastructure concerns but requires vigilance with:
- Identity and Access Management (IAM) for SaaS accounts.
- User data protection, leveraging AWS WorkDocs encryption tools for document security.
Implement Best Practices
To make the most of the AWS Shared Responsibility Model, it is essential to align effective security strategies with the requirements of specific workloads.
1. Use Advanced AWS Security Tools
AWS provides a robust suite of tools to help customers secure their environments and align with AWS security requirements.
- AWS Security Hub: Use aggregated findings for centralized compliance monitoring.
- Amazon Detective: Investigate suspicious activities using ML-assisted visualizations.
- AWS WAF and AWS Shield: Protect against web exploits and DDoS attacks.
2. Adopt Compliance as Code
Adopting a proactive approach to cloud security governance ensures you stay compliant with industry regulations.
- AWS Config: Use services like AWS Config with custom rules to automate continuous compliance checks for standards such as PCI DSS and HIPAA.
- AWS CloudFormation: Integrate compliance as code using AWS CloudFormation or Terraform templates to enforce consistent security policies across environments.
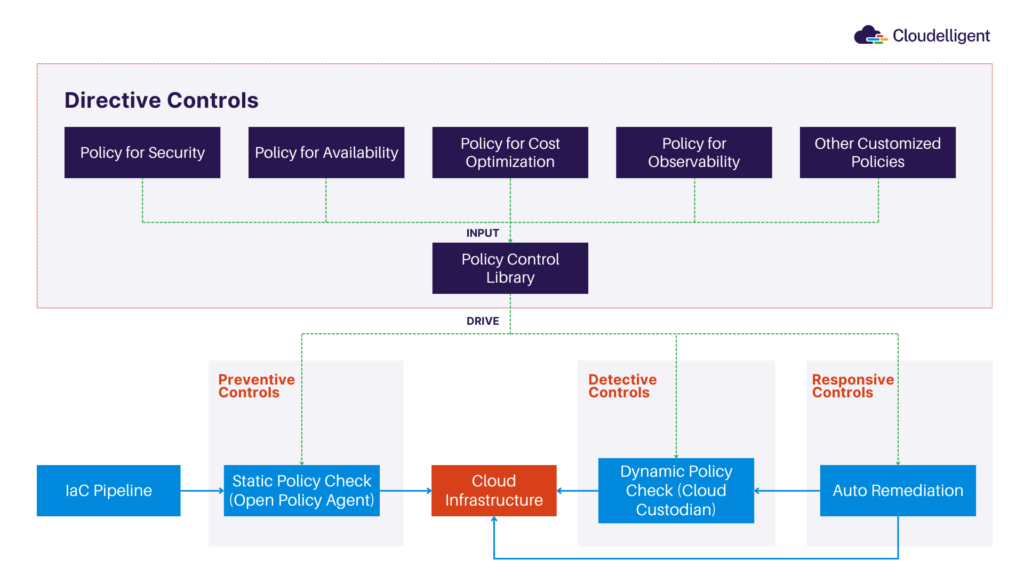
Figure 4: Compliance (Policy) as a Code (Source: aws.amazon.com)
3. Implement Holistic Monitoring
Continuous monitoring is a key component of managing security on AWS effectively.
- Amazon CloudWatch: Set up CloudWatch Alarms to detect resource spikes signaling a potential compromise.
- AWS GuardDuty: Integrate AWS GuardDuty findings into centralized Security Operations Center (SOC) workflows.
4. Prevent Misconfigurations
Misconfigurations, such as publicly exposed Amazon S3 buckets or overly permissive IAM roles, are common vulnerabilities.
- Use AWS Config Remediations to automatically correct misconfigurations in real-time.
- Regularly audit and refine access policies to ensure compliance with the AWS security best practices.
- Implement tagging strategies for resources to track ownership and enforce security standards effectively.
Industry-Specific Considerations
From compliance requirements to specialized use cases, AWS provides tailored solutions to meet the demands of different sections. By leveraging AWS security best practices and implementing robust cloud infrastructure security, organizations can align with industry regulations while maintaining a secure cloud environment.
Healthcare
- Use Amazon S3 with Object Lock for immutable medical records.
- Implement Amazon Macie for identifying sensitive data in compliance with HIPAA.
Financial Services
- AWS’s cryptographic features simplify achieving PCI DSS Level 1 compliance.
- Leverage AWS PrivateLink to ensure secure, private connections for financial APIs.
Nonprofit
- Use AWS Key Management Service (KMS) and Amazon Macie to encrypt and monitor sensitive donor and beneficiary data, ensuring compliance with GDPR and HIPAA.
- Identify and mitigate unintended public or external access to resources, safeguarding sensitive information with AWS IAM Access Analyzer.
- Optimize security costs with AWS Trusted Advisor while adhering to compliance standards like PCI DSS or ISO 27001.
- Enable secure global operations with tools like Amazon WorkSpaces for remote teams and AWS PrivateLink for private resource connectivity.
Retail
- Automate fraud detection with Amazon Fraud Detector powered by AI.
- Scale securely during peak traffic using AWS Auto Scaling with integrated CloudWatch insights.
Strengthen Your AWS Security Posture with Cloudelligent
With advanced threats and increasingly stringent regulations, understanding the AWS Shared Responsibility Model is critical for securing workloads. Misconfigurations, weak access policies, and overlooked monitoring can no longer be excused as “learning curves.”
At Cloudelligent, we specialize in fortifying AWS environments with cutting-edge security strategies tailored to your unique needs. Whether you’re securing sensitive healthcare data, processing financial transactions, or scaling retail platforms, our experts have you covered.
Take the First Step Toward Cloud Security Excellence!
Schedule your Free Cloud Security Consultation today and let us help you identify vulnerabilities, strengthen your defenses, and ensure a secure cloud environment tailored to your needs.