Migrating your workloads to AWS offers a powerful combination of cost savings and enhanced security. Businesses have reported 31% lower infrastructure costs and a 69% reduction in unplanned downtime after moving to AWS in 2024. But here’s the catch: AWS migration is only a game changer if you choose the right migration strategy. Take, for example, a financial services firm that slashed its IT expenses by 40%—this success came only after it carefully aligned its AWS migration strategy with business goals and leveraged cloud-native tools.
The key to a successful migration lies in choosing the right AWS migration strategy. Whether you opt for Lift-and-Shift, Replatforming, or Refactoring, each approach offers distinct benefits depending on your needs. Here’s a flowchart to help you select the optimal cloud migration strategy. Your migration service provider is your best ally in determining the perfect migration strategy that fits your needs.
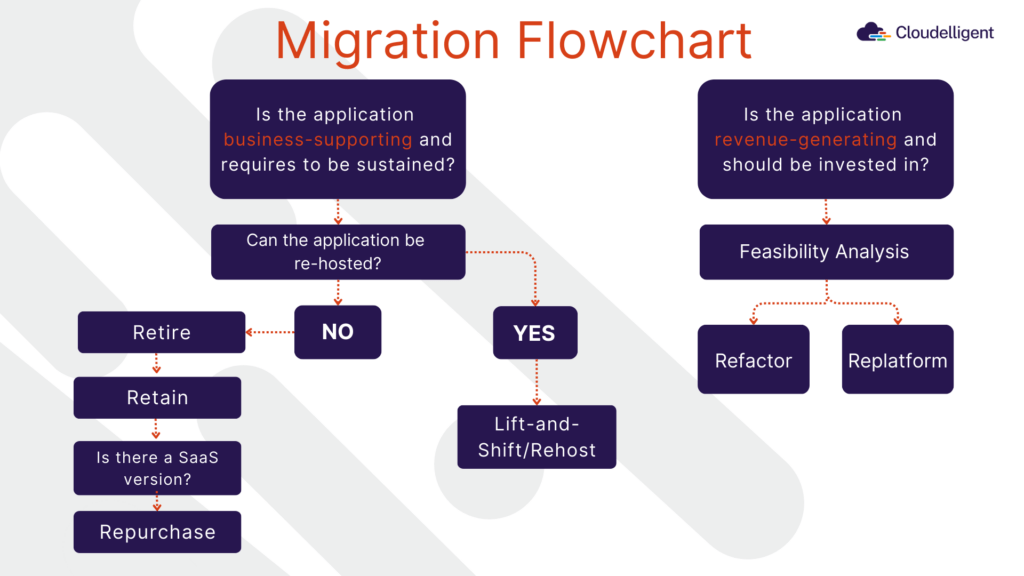
Figure 1: AWS Migration Flowchart
And let’s not forget the importance of using the right tools for a smooth transition. Check out our blog on Must-Have Tools for a Secure and Successful AWS Migration to discover the essential technologies that can ensure your AWS Migration is seamless and secure.
The Game of Clouds: Lift-and-Shift vs. Refactoring
In this blog, we’ll explore two proven AWS migration strategies: Lift-and-Shift and Refactoring backed by real-world examples to help you decide which approach aligns best with your business.
Lift-and-Shift: The Fast-Track to Migration
Looking for a fast migration solution that doesn’t require changes to your application’s architecture? Lift-and-Shift could be the perfect fit! This cloud migration strategy transfers applications from on-premises infrastructure to the cloud without any modifications. Often referred to as “rehosting,” organizations prefer this approach for its speed and simplicity, allowing for a seamless cloud transition with minimal disruption.
Several essential tools streamline Lift-and-Shift migrations. AWS App2Container containerizes your applications, making them easier to manage and scale in the cloud. AWS Data Migration Service (DMS), AWS Migration Hub, AWS Schema Conversion Tool, AWS DataSync are also some of the AWS tools used to simplify and accelerate the migration process. The image below provides a walkthrough of the different steps in the Lift-and-Shift migration strategy.
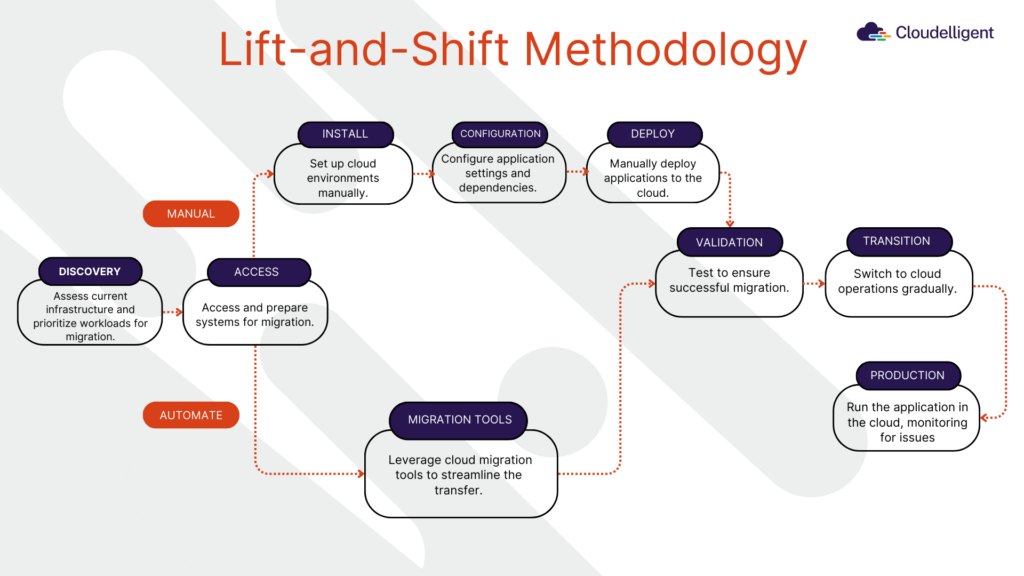
Figure 2: Lift-and-Shift Migration Path
Key Benefits of Lift-and-Shift Migrations
Lift-and-shift migrations offer a straightforward path to the cloud and provide immediate benefits without extensive changes to your applications.
- Accelerate Migration: Move swiftly to the public cloud to minimize delays in your transition.
- Lower Risk: Enjoy a safer migration experience with reduced risks compared to extensive refactoring efforts.
- Decreased Initial and Data Center Costs: By cutting initial migration and ongoing data center expenses, you can enhance your budget efficiency.
- Automated Processes: Streamline the migration process through automation, and ensure limited or no downtime for your operations.
- Foundation for Hybrid Cloud Development: Take a significant step toward creating a hybrid cloud environment, blending on-premises and cloud capabilities.
Setbacks of Lift-and-Shift Migrations
While lift-and-shift migrations offer a quick path to the cloud, they come with several potential drawbacks that need to be considered.
- Performance and Latency Issues: Legacy applications may suffer from reduced performance and increased latency after migrating to the cloud, requiring post-migration adjustments.
- Security Risks: Migrating applications without assessing vulnerabilities can transfer unaddressed security flaws to the cloud. This poses greater risks than in an on-premises environment.
- Unpredictable Costs: While lift-and-shift migration may appear cost-effective initially, ongoing expenses can shift from CapEx to OpEx. This could potentially lead to sunk costs if significant changes are needed post-migration.
Best Use Cases for Lift-and-Shift Migrations
Lift-and-shift migration is a practical approach for organizations looking to quickly transition to the cloud with minimal changes to their existing applications. Here are some of the best use cases:
- Move Applications to the Cloud Until You’re Ready to Rearchitect: Ideal for businesses that need to transition their applications to the cloud quickly but are not yet ready to invest in extensive re-architecture. This approach allows organizations to benefit from cloud resources while providing the flexibility to optimize and modernize their applications in the future.
- For Migrating Applications As-Is to the Cloud: Lift-and-Shift is particularly effective for applications that can operate effectively in their current state. Organizations can migrate legacy applications with minimal changes, preserving their functionality while leveraging the cloud’s scalability and accessibility.
- For a Cost-Effective Cloud Migration Process: This strategy enables organizations to transition quickly while minimizing upfront costs. For more insights, refer to our blog on 5 Proven Strategies for Minimizing Costs During AWS Cloud Migration, which outlines various tactics to optimize migration expenses and improve ROI.
Real-world Example of a Lift-and-Shift Migration
Real-world examples can help illustrate the effectiveness of Lift-and-Shift migrations. Aladtec, public safety employee scheduling software, faced several IT challenges with their infrastructure on ActionWeb, including lack of redundancy, limited performance visibility, manual deployment issues, and scalability constraints. Cloudelligent helped Aladtec migrate to AWS using the Lift-and-Shift methodology, resolving their IT challenges via:
- Rapid Deployment and Minimal Disruption: Cloudelligent’s Lift-and-Shift approach allowed Aladtec to quickly migrate their infrastructure from ActionWeb to AWS. This minimized downtime and disruptions to their critical public safety operations.
- Reduced Operational Costs and Increased Efficiency: By leveraging AWS’s pay-as-you-go pricing model and managed services, Aladtec was able to optimize their IT costs and eliminate the need for significant upfront investments in hardware and maintenance. Additionally, the automation capabilities of AWS simplified day-to-day operations and freed up IT resources to focus on strategic initiatives.
- Improved Reliability and Disaster Recovery: AWS’s robust infrastructure and built-in redundancy features provided Aladtec with a highly reliable and resilient platform. This significantly reduced the risk of downtime and data loss due to hardware failures or natural disasters.
- Enhanced Scalability and Flexibility: By migrating to AWS, Aladtec gained the ability to quickly scale their infrastructure up or down based on demand to ensure optimal performance and cost-efficiency during peak usage periods.
Refactoring: Building Resilient, Scalable Applications
Refactoring involves moving applications to the cloud while re-architecting them to leverage cloud-based features, flexibility, and elasticity. This cloud migration strategy requires modifying a significant portion of the code, making it more complex than other AWS migration strategies. Careful testing is needed to avoid functionality issues, and the application must be optimized for resource utilization to prevent high costs. Though refactoring is time-consuming and resource-intensive, it offers the highest ROI once fully operational.
Refactoring applications for the cloud involves using AWS tools such as AWS Lambda, Amazon RDS, and microservices architecture. AWS Lambda facilitates serverless computing which eliminates the need to manage servers, while Amazon RDS automates database tasks like scaling, backups, and maintenance. By adopting a microservices architecture with Amazon ECS or EKS, applications can scale and develop independently, enhancing agility and fault tolerance. The diagram below illustrates the key steps in the Refactor Migration Strategy.
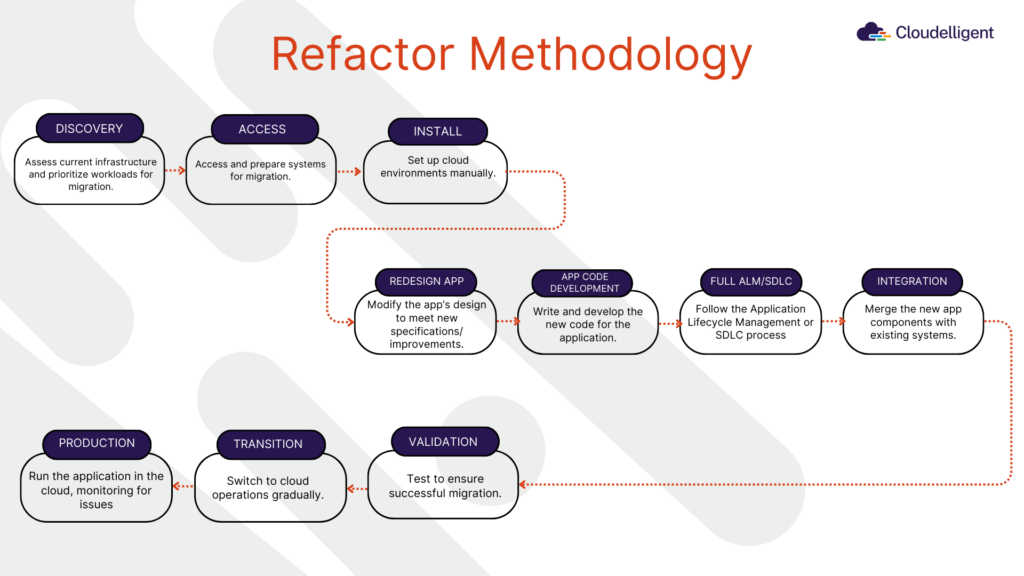
Figure 3: Refactor Migration Strategy
Key Benefits of Refactor Migrations
Refactoring offers significant advantages for migrating applications to the cloud by optimizing their architecture, performance, and scalability.
- Utilizes Cloud-Native Platform Tools: Refactoring leverages built-in cloud services and features, such as serverless computing, managed databases, and integrated monitoring. These tools enhance application performance and reduce the need for manual management of infrastructure.
- Enables Right-Sizing and Auto-Scaling: Cloud refactoring allows applications to scale automatically based on demand. This helps to ensure that only the necessary capacity is used, minimizing costs and boosting performance.
- Supports Advanced Code Factors: Refactoring leverages modern cloud-based features, such as AWS Lambda functions for serverless execution and NoSQL databases like Amazon DynamoDB. These tools optimize applications for flexibility, speed, and scalability in the cloud.
- Facilitates Decoupled Microservices Architecture: Refactoring breaks monolithic applications into smaller, independent services (microservices) that can be developed, deployed, and scaled separately. This improves agility, fault tolerance, and innovation.
Setbacks of Refactor Migrations
While refactoring offers significant advantages for optimizing applications in the cloud, it also presents potential challenges that organizations should carefully consider.
- Vendor Lock-In: Refactoring applications for a specific cloud provider can lead to vendor lock-in. This may create a dependence on that provider’s technology and services, limiting flexibility and increasing cost.
- Requires Advanced DevOps Skills: The refactoring process often demands advanced DevOps expertise. Organizations may need to invest in training or hire specialized talent proficient in cloud architecture, automation tools, and CI/CD pipelines.
- May Require More Time: While refactoring can yield significant benefits, it is typically a time-consuming process. Modifying existing codebases, testing for functionality, and ensuring compatibility with cloud services can extend project timelines.
- Compatibility Issues: Compatibility issues might result in refactored applications and existing systems, tools, or third-party services. Organizations must thoroughly assess integration points to avoid disruptions and ensure seamless.
- Scope Creep: As additional features or enhancements are added during refactoring, the initial project scope can expand unintentionally. This may result in increased complexity, extended timelines, and inflated costs.
Best Use Cases for Refactor Migrations
Refactor migration is ideal for organizations looking to optimize their applications for the cloud, enhancing performance, scalability, and efficiency. Some of the best use cases are:
- Adding Features, Scaling, or Enhancing Performance: If your business requires rapid addition of features to meet evolving customer demands refactoring can be an ideal solution. By re-architecting applications to leverage cloud-native capabilities, you can enhance performance and ensure the application can scale efficiently allowing business agility and responsiveness to market changes.
- Prioritizing Efficiency: In scenarios where operational efficiency is paramount, refactoring helps streamline application performance and resource usage. This is particularly beneficial for businesses aiming to maximize ROI while improving application responsiveness and user experience.
- Scaling Existing Applications: If you have legacy applications that struggle to handle increasing workloads, refactoring offers a path to modernize and scale these systems effectively. This cloud migration strategy also enhances the ability to deploy updates and maintain uptime during high-demand periods.
Real-world Example of a Refactor Migration
Real-world examples can vividly illustrate the effectiveness of refactor migrations. Cloudelligent employed a refactor migration approach for a beverage manufacturing company to transform their wine manufacturing and inventory application from a complex monolithic system into microservices. This approach offered several key benefits:
- Enhanced Scalability: Microservices enable the independent scaling of individual components. This significantly improves overall system performance and capacity to handle varying loads.
- Improved Maintainability: Smaller, focused services are much easier to manage, update, and troubleshoot compared to a large monolithic application which streamlines maintenance efforts.
- Increased Flexibility: With microservices, you can deploy new features and updates more quickly, as changes to one service won’t impact the entire system, allowing for faster innovation.
- Better Fault Isolation: If an issue arises in one microservice, it’s less likely to affect others while enhancing system reliability and minimizing downtime.
Questions to Ask When Choosing a Migration Strategy
When planning a cloud migration, it’s crucial to consider various factors to ensure a smooth and successful transition. Here are some key questions to guide your decision-making process:
- What are our primary business goals for this migration?
(Are we aiming to reduce costs, improve performance, enhance scalability, or foster innovation?)
- How complex are the workloads we plan to migrate?
(Do any applications require a tailored approach due to their complexity?)
- What are our time and budget constraints for this migration?
(Do we have the resources and timeline necessary for the desired cloud migration strategy?)
- What are our team’s technical capabilities?
(Do we have the necessary skills and experience with cloud technologies, or do we need to invest in training?)
- What is our organization’s risk tolerance?
(Are we willing to take on higher risks associated with significant changes, or do we prefer a more gradual migration?)
- What application dependencies do we need to consider?
(Are there applications that rely on each other that must be migrated together or in a specific sequence?)
- What regulatory and compliance requirements do we need to address?
(Are there specific regulations governing our data and applications that we must adhere to during migration?)
- How will this migration support our future scalability and innovation?
(Does our chosen migration strategy enable easy scaling and adaptability to meet changing market demands and technological advancements?)
Migration Planning With Cloudelligent: Which is the Right Fit for You?
Kickstart your cloud journey with a rock-solid migration strategy crafted just for your business! Our customized approach ensures that every need is met, setting you up for unparalleled success. With Cloudelligent’s impressive track record of guiding successful migrations, you can trust our expertise to streamline your transition—your cloud adventure awaits!
You can start with our expert-led Migration Readiness Assessment (MRA) to uncover challenges and seize opportunities, paving the way for a smooth and seamless transition to the cloud.