Are you planning to migrate your applications to a public cloud, to start a project requiring scalability and fault tolerance? It’s time to think about cloud security and how to handle it.
In classical IT, we must first differentiate between infrastructure security and application security, at AWS, it is up to the provider to manage this infrastructure security.
Cloud computing makes it easy to adapt products to demand, but the security of these products is critical and should not be overlooked. To do this, public cloud providers offer a fairly complete range of tools that can be used.
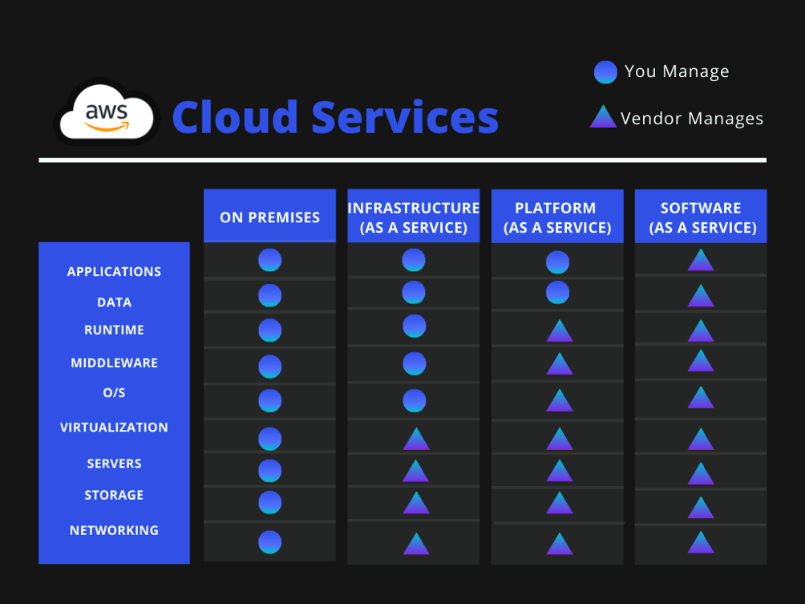
Depending on your choice of provider, you will have more or less IaaS (Infrastructure as a Service), PaaS (Platform as a Service) or SaaS (Software as a Service) services.
Working with sensitive customer data is essential for most contact centers, making privacy and security a top concern. But since Amazon Connect is a cloud contact center product, Amazon considers security and compliance to be shared between AWS and its customers and adopts a common policy called the Shared Responsibility Model. Each AWS customer should examine in detail the shared responsibility model, which varies for each AWS service, but the bulk of it is captured in the Amazon graph below:
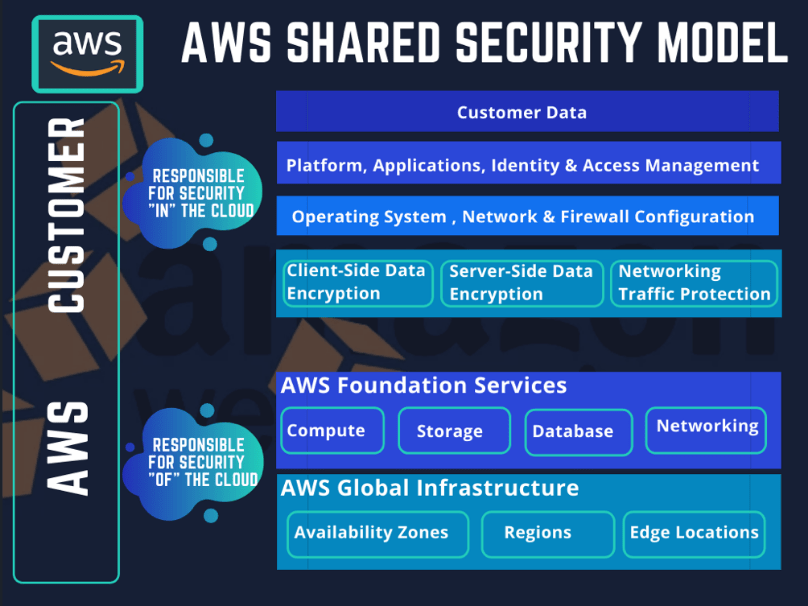
Typically, AWS manages the security and compliance of its infrastructure, including the hardware and software that run AWS services in the cloud. Customers must manage the security and compliance of everything they host in the AWS service (s) they choose, including customer and customer data, encryption, security fixes, system, etc.
The shared responsibility model differs by type of service, however. There are three categories of service types: infrastructure services, container services, and abstract services. Let’s compare the three categories of service type and how the security and compliance property varies between them.
Infrastructure Services
An infrastructure service is a type of IT service where the infrastructure that traditionally exists in a local data center is hosted by a provider (in this case, AWS) in the cloud.
For infrastructure services, AWS is responsible for:
• Basic services (network, storage, processing)
• AWS global infrastructure
• AWS Identity and Access Management
• AWS API endpoints